The study of volatile chemicals from humans has recently attracted increasing attention, particularly regarding the potential of breath volatiles to rapidly and non-invasively diagnose diseases such as cancer.
Why use breath monitoring?
Biological monitoring is well-established for assessing personal exposure to chemicals, but recent research is now showing its potential to assist understanding of medical conditions more generally.
However, traditional blood and urine monitoring is invasive, and often requires complex sample preparation prior to GC analysis. Using breath monitoring instead solves these problems, and has the potential to allow rapid point-of-care highlighting of a range of medical conditions.
What conditions are being investigated?
The literature around breath-based disease diagnosis is extensive, with recent papers on various cancers, asthma, pulmonary disease, respiratory conditions, liver disease and kidney disease, to name but a few.
In addition, an important aspect of research in this area involves investigating natural variability in breath profiles, and the effect of external factors such as diet and environment.
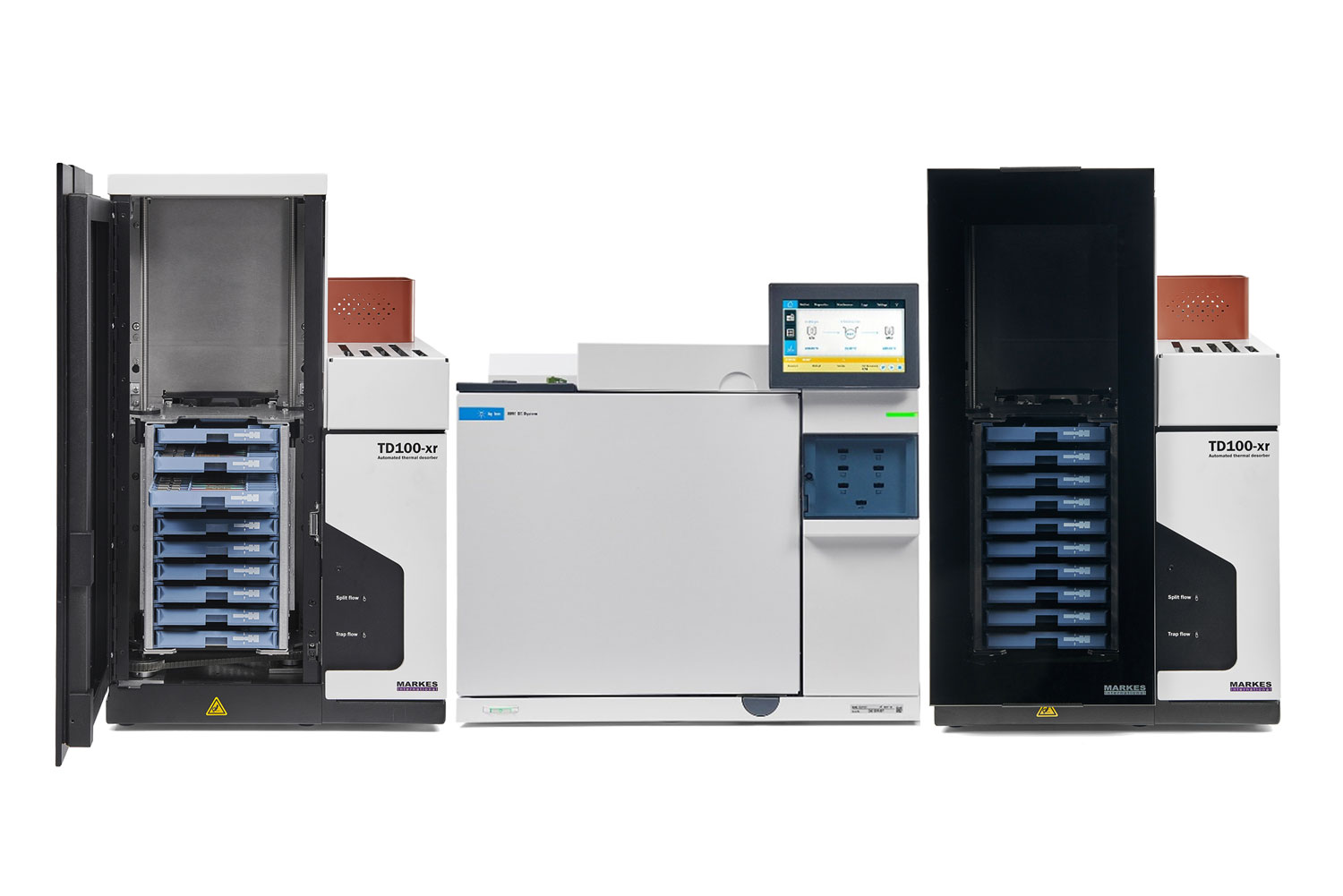
The benefits of thermal desorption for breath monitoring

Capturing breath volatiles directly onto sorbent tubes, with analysis by thermal desorption, completely circumvents laborious sample preparation (and consequent potential bias) common with techniques such as solvent extraction of aqueous samples.
In addition, modern thermal desorbers allow multi-bed tubes and traps to be used, widening the range of compounds that can be reliably monitored from a single sample.